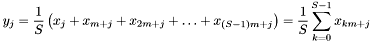
The function implemented by this node is given by:
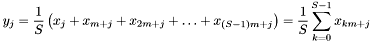
In other words, it slices the input vector 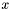 into several subvectors of size
into several subvectors of size  and sums them up, divided by the total amount of resulting pieces
and sums them up, divided by the total amount of resulting pieces 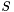 . Remember that
. Remember that  is the output size.
is the output size.
If the input vector's size isn't a multiple of the output vector's size, that is, if  can't be written as
can't be written as 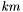 , then the last vector slice will consider only the remaining terms, e.g. if
, then the last vector slice will consider only the remaining terms, e.g. if 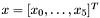 and
and 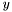 is of size
is of size  then
then
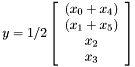
Schematically, this idea can be depicted as

The function's gradient is:

Functions | |
| int | gnn_convergence_f (gnn_node *node, const gsl_vector *x, const gsl_vector *w, gsl_vector *y) |
| Computes the output. | |
| int | gnn_convergence_dx (gnn_node *node, const gsl_vector *x, const gsl_vector *w, const gsl_vector *dy, gsl_vector *dx) |
Computes 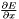 .
. | |
| int | gnn_convergence_dw (gnn_node *node, const gsl_vector *x, const gsl_vector *w, const gsl_vector *dy, gsl_vector *dw) |
Computes  .
. | |
| gnn_node * | gnn_convergence_new (size_t input_size, size_t output_size) |
| Creates an input convergence node. | |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 203 of file gnn_convergence.c. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 159 of file gnn_convergence.c. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 114 of file gnn_convergence.c. |
|
||||||||||||
|
This function creates a node of the gnn_divergence : Input Divergence. type.
Definition at line 229 of file gnn_convergence.c. |
 1.2.18
1.2.18