

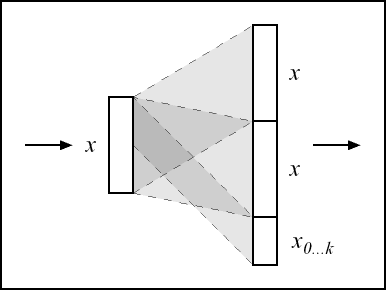
In other words, it replicates the input several times on the output vector. If the output vector's size isn't a multiple of the input vector's size, that is, if  can't be written as
can't be written as 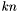 , then only the first inputs will be copied, e.g. if
, then only the first inputs will be copied, e.g. if 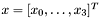 and
and 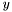 is of size
is of size  then
then
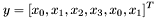
Schematically, this idea can be depicted as
The function's gradient is:

Typedefs | |
| typedef _gnn_convergence | gnn_convergence |
| The structure for a gnn_divergence : Input Divergence. node. | |
| typedef _gnn_divergence | gnn_divergence |
| The structure for a gnn_divergence : Input Divergence. node. | |
Functions | |
| int | gnn_divergence_f (gnn_node *node, const gsl_vector *x, const gsl_vector *w, gsl_vector *y) |
| Computes the output. | |
| int | gnn_divergence_dx (gnn_node *node, const gsl_vector *x, const gsl_vector *w, const gsl_vector *dy, gsl_vector *dx) |
Computes 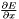 .
. | |
| int | gnn_divergence_dw (gnn_node *node, const gsl_vector *x, const gsl_vector *w, const gsl_vector *dy, gsl_vector *dw) |
Computes  .
. | |
| gnn_node * | gnn_divergence_new (size_t input_size, size_t output_size) |
| Creates an input divergence node. | |
|
|
This datatype holds the information for a gnn_divergence : Input Divergence. node. Basically, it extends the gnn_node with special pointers to get fast accesses to the needed vector slices. Definition at line 48 of file gnn_convergence.h. |
|
|
This datatype holds the information for a gnn_divergence : Input Divergence. node. Basically, it extends the gnn_node with special pointers to get fast accesses to the needed vector slices. Definition at line 48 of file gnn_divergence.h. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 191 of file gnn_divergence.c. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 145 of file gnn_divergence.c. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Definition at line 102 of file gnn_divergence.c. |
|
||||||||||||
|
This function creates a node of the gnn_divergence : Input Divergence. type.
Definition at line 217 of file gnn_divergence.c. |
 1.2.18
1.2.18