Functions
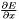 evaluation function.
evaluation function. 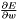 evaluation function.
evaluation function. 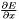 recursively.
recursively. 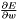 recursively.
recursively. What is the Extension API's purpose?
The Extension API has been designed in order to provide a framework to include custom node types, i.e. nodes that compute a specific function that isn't included in the libgnn distribution.
The node types included in the distribution have also been built upon this programming interface.
Basics
Creating a new node type requires the programmer to implement at least 4 functions, which describe/incarnate the behaviour of the node, and are attached to the new node type.
All node types should built upon a basic node type: the gnn_node. The C structure which will implement the node type should contain, as it's first field, a gnn_node, followed by the additional data field the node might need. Per example:
// it's always nice to have a type definition typedef struct _myNodeType myNodeType; // the structure definition struct _myNodeType { gnn_node node; // the underlying gnn_node // now comes the rest int exampleField1; double exampleField2; ... }
To create a custom node, you should provide a constructor. The constructor should take the needed info to describe your new instance fully. The constructor should allocate memory for the new structure, and initialize the underlying gnn_node, by calling the gnn_node_init function:
Example for an Atomic Node Type:
// you should return a gnn_node pointer to the new instance gnn_node * my_node_new (int input_size, int output_size, int param_size, ...) { gnn_node *node; myNodeType *mynode; // allocate memory for your node type mynode = (myNodeType *) malloc (sizeof (myNodeType)); // get a pointer to the instance, but viewed as a gnn_node : node = (gnn_node *) mynode; // call the initialization function gnn_node_init ( node, "myNodeType", my_node_type_f, my_node_type_dx, my_node_type_dw, my_node_type_dest ); // if this node were a constructor node, // then install the subnodes HERE! In example, calling // gnn_node_sub_install_node_vector ... // initialize the node sizes gnn_node_set_sizes (node, input_size, output_size, param_size); // initialize the rest your node type might need ... // finally, return a pointer to the your instance as a gnn_node return node; }
The gnn_node_init function takes a pointer to the node, a string which describes the node type, plus 4 additional functions:
Coding Standards
The libgnn library has been coded respecting a coding standard that hasn't been documented yet :-) . But basically, you should look at its source code and try to code as similar as posible. Some things you must respect:
h and a .c file. The first should contain the public interface definition, and the second, the implementation. Always protect the header file with #ifdef construct from multiple inclusion. The implementation should depend only on those files that it really needs.Functions | |
| void | gnn_node_destroy_structure (gnn_node *node) |
| Destroys a gnn_node. | |
| int | gnn_node_default_f (gnn_node *node, const gsl_vector *x, const gsl_vector *w, gsl_vector *y) |
| Default evaluation function. | |
| int | gnn_node_default_dx (gnn_node *node, const gsl_vector *x, const gsl_vector *w, const gsl_vector *dy, gsl_vector *dx) |
Default 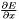 evaluation function.
evaluation function. | |
| int | gnn_node_default_dw (gnn_node *node, const gsl_vector *x, const gsl_vector *w, const gsl_vector *dy, gsl_vector *dw) |
Default 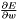 evaluation function.
evaluation function. | |
| void | gnn_node_default_destructor (gnn_node *node) |
| Default gnn_node destructor. | |
| int | gnn_node_init (gnn_node *node, const char *type, gnn_node_f f, gnn_node_df dx, gnn_node_df dw, gnn_node_destructor dest) |
| Initializes a gnn_node structure. | |
| int | gnn_node_set_sizes (gnn_node *node, int n, int m, int l) |
| Set the node's sizes. | |
| gsl_vector * | gnn_node_local_get_w (gnn_node *node) |
| Get local parameters. | |
| gsl_vector * | gnn_node_local_get_dw (gnn_node *node) |
| Get local parameter gradients. | |
| gsl_vector_int * | gnn_node_local_get_f (gnn_node *node) |
| Get local parameters frozen flags. | |
| int | gnn_node_local_update (gnn_node *node) |
| Get local parameters. | |
| int | gnn_node_eval_f (gnn_node *node, const gsl_vector *x, gsl_vector *y) |
| Evaluates the output of the function recursively. | |
| int | gnn_node_eval_dx (gnn_node *node, const gsl_vector *dy, gsl_vector *dx) |
Evaluates 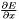 recursively.
recursively. | |
| int | gnn_node_eval_dw (gnn_node *node) |
Evaluates 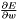 recursively.
recursively. | |
|
|
This is the default destructor for a gnn_node when initialized with NULL in gnn_node Extension API. It asumes that the current gnn_node type hasn't allocated any additional memory nor contains any other specific info other than a gnn_node's default. Consecuently, it doesn't anything than just return.
Definition at line 352 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This is the default 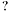
Definition at line 329 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This is the default 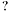
Definition at line 299 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
This is the default evaluation function for a gnn_node when initialized with NULL in gnn_node Extension API. It computes 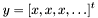
that is, it copies the input vector
Definition at line 252 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
|
This function destroys the underlying gnn_node structure by freeing the memory associated to the fields of the node and freeing the structure itself. It also calls the gnn_node : Basic Building Block for Gradient Machines. function on all subnodes. This function should not be called directly. Instead, gnn_node : Basic Building Block for Gradient Machines. should be called instead in order to free also additional resources that could have been allocated specifically for the node's type. Please read also the details available in gnn_node : Basic Building Block for Gradient Machines.'s documentation.
Definition at line 209 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
|
This function calls the installed gnn_node::dw function with the appropiate arguments. This function should only be called from construction node's evaluation functions. If you want to evaluate it from outside, you should call \gnn_node_eval_dw instead, which initiates the recursion parameters appropiatelly.
Definition at line 1425 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
This function calls the installed gnn_node::dx function with the appropiate arguments. This function should only be called from construction node's evaluation functions. If you want to evaluate it from outside, you should call \gnn_node_eval_dx instead, which initiates the recursion parameters appropiatelly.
Definition at line 1388 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
This function calls the installed gnn_node::f function with the appropiate arguments. This function should only be called from construction node's evaluation functions. If you want to evaluate it from outside, you should call \gnn_node_eval_f instead, which initiates the recursion parameters appropiatelly.
Definition at line 1354 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This function initializes a gnn_node structure. The memory for the structure should be allocated manually. The sizes should be set after calling this function. An example of its use is the following:
gnn_node * gnn_mifunction (int input_size, int output_size, int param_size) { gnn_node *node; node = (gnn_node *) malloc (sizeof (*node)); gnn_node_init ( node, "gnn_mifunction", gnn_mifunction_f, gnn_mifunction_dx, gnn_mifunction_dw, gnn_mifunction_dest); gnn_node_set_sizes (input_size, output_size, param_size); // initialize the rest ... If one of the function pointers is NULL, then it installs the default functions:
Definition at line 1183 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
|
This function returns a pointer to the node's own parameters gradient
Definition at line 1292 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
|
This function returns a pointer to the node's own parameters frozen flags. The returning vector is the flags vector itself and its values can be freely changed. When finished, call gnn_node Extension API. The values should be binary: 0 means that the parameter is free, and 1 (non-zero) means that the parameter is frozen (fixed).
Definition at line 1313 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
|
This function returns a pointer to the node's own parameters. The returning vector is the parameter vector itself and its values can be freely changed. When finished, call gnn_node Extension API.
Definition at line 1272 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
|
This function updates the local parameters and its changes. This function should be called after any change in the parameters to make them effective.
Definition at line 1330 of file gnn_node.c. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
This function sets the node's sizes for its input, output and parameter vector. It should be called after calling the gnn_node Extension API (and the gnn_node Subnodes API in case of a constructor node) function.
Definition at line 1241 of file gnn_node.c. |
 1.2.18
1.2.18